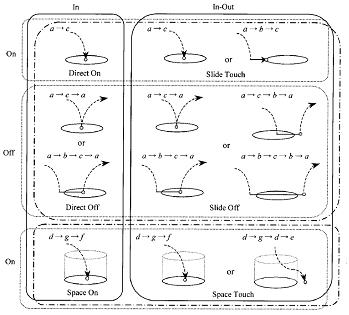
In this study two experiments were conducted to compare pen-based selection strategies and their characteristics. Two state transition models were also formulated which provide new vocabulary that will help in investigating interactions related to target selection issues. Six strategies, which can be described by the state transition models, were used in the experiments. We determined the best strategy of the six to be the ˇ°Slide Touchˇ± strategy, where the target is selected at the moment the pen-tip touches the target for the first time after landing on the screen surface. The six strategies were also classified into strategy groups according to their characteristics. We determined the best strategy group to be the ˇ°In-Outˇ± strategy group, where the target is selected by contact either inside or outside the target. Analyses show that differences between strategies are influenced by variations in target size; however, the differences between strategies are not affected by the distance to the target (i.e., pen-movement-distance) or the direction of pen movement (i.e., pen-movement-direction). We also found ˇ°the smallest maximum sizeˇ± of five pixels, i.e., the boundary value for the target size below which there are significant differences, and above which there are no significant differences between the strategies in error rate. Relationships between interaction states, routes, and strategy efficiency were also investigated.
Publications:
Ren, X., and Moriya, S. 2000. Improving selection performance on pen-based system: A study of pen-based interaction for selection tasks, ACM Trans. Computer-Human Interaction, Vol.7, No.3. pp. 384-416. PDF
![]()